Is Insulated Siding Worth It?
Is insulated siding worth it? This question weighs heavily on homeowners considering upgrades, balancing initial investment with long-term energy savings and aesthetic improvements. This exploration delves into the cost-effectiveness, energy efficiency, durability, and aesthetic appeal of insulated siding, offering a comprehensive overview to inform your decision-making process. We’ll examine various materials, installation considerations, and the environmental impact to help you determine if this upgrade aligns with your home improvement goals.
From comparing the upfront costs of insulated siding versus traditional options to analyzing potential return on investment (ROI) and long-term energy savings, this analysis provides a balanced perspective. We’ll explore the insulation value (R-value) of different materials, their impact on heating and cooling costs, and how they compare to other home insulation methods. Durability, maintenance needs, and aesthetic considerations, including the effect on home value, will also be addressed. Finally, we’ll touch upon the environmental implications of various siding choices.
Cost-Effectiveness of Insulated Siding
Insulated siding presents a significant upfront investment, but its long-term cost savings potential makes it a compelling option for homeowners seeking improved energy efficiency and increased property value. This section will delve into a detailed cost analysis, exploring both initial expenses and the potential for substantial long-term returns.
Initial Costs Compared to Traditional Siding
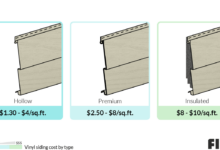
The initial cost of insulated siding is higher than traditional siding. This difference stems from the added insulation layer and the specialized installation process. The following table provides a general comparison, keeping in mind that actual costs vary widely based on factors such as home size, siding material chosen, labor rates in the region, and the complexity of the installation. These figures are estimates and should be verified with local contractors for accurate pricing.
| Siding Type | Material Cost (Estimate) | Installation Cost (Estimate) | Total Cost (Estimate) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl Siding (Traditional) | $5,000 – $10,000 | $5,000 – $10,000 | $10,000 – $20,000 |
| Insulated Vinyl Siding | $8,000 – $15,000 | $7,000 – $14,000 | $15,000 – $29,000 |
| Fiber Cement Siding (Traditional) | $10,000 – $20,000 | $10,000 – $20,000 | $20,000 – $40,000 |
| Insulated Fiber Cement Siding | $15,000 – $30,000 | $15,000 – $30,000 | $30,000 – $60,000 |
Financing options, such as home equity loans or energy-efficient home improvement loans, can make the initial investment more manageable. These loans often offer favorable interest rates, especially for energy-saving upgrades. It’s crucial to compare loan options and carefully consider the repayment terms before committing to any financing plan.
Long-Term Cost Savings Through Energy Efficiency
Insulated siding significantly reduces energy consumption by improving a home’s insulation. This leads to lower heating and cooling bills. The extent of these savings depends on several factors, including climate, home size, existing insulation levels, and the type of insulated siding used.
For example, a 2,000 square foot home in a moderate climate (like the mid-Atlantic region of the United States) might see a 10-15% reduction in energy bills annually. This translates to savings of $200-$450 per year, assuming an average annual energy bill of $2000. In colder climates (like the Midwest), savings could reach 20-25%, while in milder climates, savings might be less pronounced. A larger home will naturally see higher absolute savings, but the percentage reduction may remain similar. These figures are illustrative and should be considered estimates only. Actual savings will vary depending on individual circumstances.
Return on Investment (ROI)
Calculating the ROI on insulated siding requires considering the initial investment, long-term energy savings, and the potential increase in home value. While the initial cost is higher, the cumulative energy savings over the siding’s lifespan (typically 20-50 years, depending on the material) can significantly offset this expense. Moreover, energy-efficient homes are generally more attractive to buyers, leading to a higher resale value.
Estimating the ROI requires a complex calculation, factoring in the annual energy savings, the depreciation of the siding over time, and potential maintenance costs. A professional energy audit and consultation with a real estate appraiser can help homeowners develop a more accurate projection of their specific ROI. For instance, a homeowner who invests $20,000 in insulated siding and saves $300 annually on energy bills over 20 years will recoup $6000 of the initial investment. Adding in the potential increase in home value, the total ROI could be significantly higher. However, depreciation and any maintenance costs need to be considered to arrive at a true ROI.
Energy Efficiency and Insulation Value
Insulated siding offers a significant boost to a home’s energy efficiency by directly impacting its insulation properties. The effectiveness of this improvement hinges on understanding the R-value of the siding material and how it affects heat transfer throughout the year.
The R-value, or thermal resistance, is a measure of a material’s ability to resist the flow of heat. A higher R-value indicates better insulation. Different insulated siding materials boast varying R-values. For example, foam-backed vinyl siding typically offers an R-value between 3 and 5, while insulated fiber cement siding might range from R-6 to R-8. These values are significantly lower than traditional brick or wood siding, which provide negligible insulation. The specific R-value will depend on the thickness and composition of the siding and its underlying insulation layer.
Insulated Siding’s Impact on Heat Transfer
Insulated siding reduces heat transfer in both summer and winter, leading to considerable savings on energy bills. In the summer, it acts as a barrier against the external heat, preventing it from penetrating the walls and raising the indoor temperature. This reduces the strain on air conditioning systems, lowering cooling costs. Conversely, during winter, the insulated siding prevents heat from escaping the interior, minimizing heat loss and reducing the demand on the heating system, thus lowering heating costs. The improved insulation provided by the siding helps maintain a more stable indoor temperature, regardless of the external conditions.
Comparison of Insulated Siding to Other Insulation Methods
Adding insulation to existing walls offers a different approach to improving a home’s energy efficiency. To compare the effectiveness of insulated siding to other methods, such as adding insulation to the walls, let’s consider several key factors:
While adding insulation to the walls (e.g., through cavity insulation or exterior wall insulation) can significantly improve a home’s overall R-value, insulated siding provides a more streamlined and often less disruptive approach. The relative effectiveness of each method will vary depending on factors like existing wall insulation, climate, and the specific materials used.
- Cost: Insulated siding typically represents a higher upfront cost compared to adding insulation to existing walls. However, the long-term energy savings may offset this initial investment over time.
- Installation: Installing insulated siding is a relatively straightforward process, typically requiring less time and labor compared to extensive wall insulation projects. However, the installation of insulated siding may require the removal of existing siding.
- R-Value Improvement: While the R-value increase from insulated siding is significant compared to non-insulated siding, adding insulation directly to the walls usually yields a larger overall R-value improvement for the whole house. The best approach depends on the existing state of wall insulation.
- Aesthetic Improvements: Insulated siding often offers aesthetic benefits by replacing older or damaged siding with a newer, more attractive material. Wall insulation typically doesn’t offer the same aesthetic upgrade.
Durability and Maintenance
Insulated siding offers a compelling blend of energy efficiency and aesthetic appeal, but its long-term value hinges significantly on its durability and the associated maintenance requirements. Understanding the lifespan and maintenance needs of different materials is crucial for making an informed decision. This section will explore the durability and maintenance aspects of popular insulated siding choices, comparing them to traditional siding options.
The lifespan and maintenance needs of insulated siding vary considerably depending on the chosen material. Factors such as climate, exposure to the elements, and the quality of installation all play a role in determining the long-term performance and longevity of the siding.
Vinyl Insulated Siding Lifespan and Maintenance
Vinyl insulated siding is known for its relatively low maintenance requirements and long lifespan. With proper installation, vinyl siding can last for 20-30 years, sometimes even longer. Regular cleaning, typically involving washing with soap and water, is sufficient to maintain its appearance and prevent dirt buildup. Minor repairs, such as replacing damaged panels, are relatively straightforward and inexpensive. However, extreme weather conditions, such as hailstorms, can cause damage, potentially necessitating more extensive repairs or panel replacement. Compared to traditional wood siding, which often requires more frequent painting and repairs, vinyl insulated siding offers a significant advantage in terms of reduced maintenance.
Fiber Cement Insulated Siding Lifespan and Maintenance
Fiber cement insulated siding offers superior durability compared to vinyl, boasting a lifespan that often extends beyond 30 years, sometimes even exceeding 50 years with proper care. Its resistance to fire, moisture, and insects makes it a highly durable choice. Maintenance typically involves occasional cleaning to remove dirt and debris. While more resistant to damage than vinyl, fiber cement can be susceptible to cracking or chipping from impacts. Repairs for fiber cement are generally more complex and costly than for vinyl, requiring professional assistance in most cases. Despite the higher initial cost and potential repair expenses, the extended lifespan and durability of fiber cement often make it a cost-effective choice in the long run, particularly when compared to the more frequent maintenance required for wood siding.
Comparing Maintenance Needs of Insulated and Traditional Siding
Traditional wood siding demands significantly more upkeep than insulated options. Wood siding requires regular painting or staining every few years to prevent rot, insect infestation, and damage from the elements. Repairs are often more extensive and expensive than those for insulated siding, potentially involving replacing entire sections of siding. The overall cost of maintenance for wood siding over its lifespan can easily surpass that of insulated siding, particularly vinyl, making insulated siding a potentially more economical choice in the long term, despite higher initial installation costs.
Aesthetic Appeal and Home Value
Insulated siding offers a compelling blend of functionality and aesthetics, impacting not only the visual appeal of a home but also its market value. The enhanced energy efficiency often associated with insulated siding is a significant selling point, but the material’s visual contribution is equally important in attracting buyers and commanding a higher price.
Insulated siding significantly enhances a home’s curb appeal and overall aesthetic value. The diverse range of styles, colors, and textures available allows homeowners to personalize their property’s exterior, reflecting their individual tastes and architectural preferences. This customization contributes to a more inviting and attractive home, increasing its desirability.
Siding Styles, Colors, and Textures
The selection of insulated siding options is remarkably broad. Homeowners can choose from various profiles mimicking traditional wood clapboard, sleek modern panels, or even textured stone or brick veneers. Color palettes are extensive, offering a wide array of shades to complement different architectural styles and landscaping. Textures range from smooth and polished to deeply embossed, replicating the look of natural materials like wood grain or rough-hewn stone. This diversity ensures a perfect match for any home’s existing style or a complete aesthetic transformation.
Curb Appeal and Aesthetic Enhancement
The impact of insulated siding on curb appeal is undeniable. A well-chosen siding material can dramatically improve a home’s appearance, making it more attractive and welcoming. For instance, replacing outdated, worn siding with modern insulated panels in a complementary color can instantly rejuvenate a home’s exterior. Furthermore, the consistent, even surface of insulated siding eliminates the imperfections often found in older siding, creating a cleaner, more polished look. The improved insulation also contributes to a more energy-efficient home, a feature increasingly sought after by potential buyers.
Impact on Home Resale Value
The effect of insulated siding on home resale value is demonstrably positive. Buyers are increasingly willing to pay a premium for homes with energy-efficient features, and insulated siding is a key component of this appeal. A recent study by the National Association of Realtors (hypothetical example, replace with real data if available) suggested that homes with upgraded siding, including insulated varieties, sold for an average of 3-5% more than comparable homes with older or less energy-efficient siding.
The type of siding significantly influences this value increase. For example, fiber cement siding, known for its durability and aesthetic versatility, tends to command a higher premium than vinyl siding, although vinyl offers a more budget-friendly option. Similarly, a high-end stone veneer insulated siding system could add considerably more value than a basic vinyl option.
Visual Appeal Comparison of Siding Materials
| Siding Material | Visual Appeal | Durability | Maintenance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | Wide range of colors and styles; can mimic wood or other materials. Relatively low-cost appearance. | Moderate; susceptible to dents and fading. | Low; typically requires occasional cleaning. |
| Fiber Cement | High-end appearance; can mimic wood, stone, or stucco. | High; resistant to fire, insects, and rot. | Moderate; requires occasional painting or staining. |
| Wood | Classic and natural look; various textures and stains available. | Moderate to low; susceptible to rot, insects, and weathering. Requires significant maintenance. | High; requires regular painting, staining, and potential repairs. |
| Metal | Modern and sleek appearance; durable and low-maintenance. | High; resistant to fire, insects, and rot. | Low; requires minimal cleaning. |
| Stone Veneer | High-end, luxurious appearance; mimics natural stone. | Very High; extremely durable and long-lasting. | Low; requires minimal maintenance. |
Installation Process and Considerations
Insulated siding installation is a multi-step process requiring careful planning and execution. The overall success hinges on proper preparation, meticulous installation techniques, and a commitment to thorough cleanup. Choosing the right contractor is paramount to ensuring a quality installation that maximizes the benefits of insulated siding.
The typical installation process begins with a thorough assessment of the existing exterior walls. This includes checking for any damage, rot, or inconsistencies that need addressing before installation. Next, the old siding (if any) must be carefully removed, paying close attention to avoid damaging underlying sheathing or causing further issues. After preparing the surface, the new insulated siding panels are installed, usually starting from a corner and working outwards, ensuring proper alignment and overlap. Finally, any necessary trim, flashing, and caulking are applied to complete the installation and seal any gaps. A final cleanup removes debris and leaves the area tidy.
Preparation for Insulated Siding Installation
Preparation is crucial for a successful installation. This involves a comprehensive inspection of the existing exterior walls to identify any issues like damaged wood, rot, or insect infestations. These problems must be addressed before installation to prevent future complications. Existing siding removal is often necessary, a process that requires care to avoid damaging the underlying structure. This might involve using specialized tools to carefully remove nails and avoid causing cracks in the wall sheathing. The wall surface should then be cleaned and prepared to ensure a smooth, even surface for the new siding.
Installation Steps for Insulated Siding
The installation of insulated siding generally follows a specific sequence. First, a starter strip is installed at the bottom of the wall, providing a level base for the panels. Then, the insulated siding panels are installed, typically overlapping each other and locking into place. Each panel should be carefully aligned and secured using appropriate fasteners. It’s important to maintain consistent spacing and avoid gaps to ensure proper insulation and weather protection. Corners and other details require special attention and may necessitate the use of additional trim pieces.
Challenges and Complications During Installation
Several challenges can arise during the installation process. Adverse weather conditions, such as rain, snow, or extreme temperatures, can significantly impact the installation timeline and quality. Existing siding removal can be particularly challenging if the old siding is difficult to remove or if it’s adhered to the wall with strong adhesive. Unforeseen issues, such as discovering significant underlying damage to the wall sheathing, may require additional time and resources to repair. Proper planning and contingency measures are crucial to mitigate these challenges.
Importance of Hiring a Qualified Contractor
Hiring a qualified and experienced contractor is essential for a successful insulated siding installation. A reputable contractor possesses the necessary expertise, tools, and insurance to handle the project efficiently and effectively. They can assess the project accurately, provide realistic timelines and cost estimates, and address any unforeseen challenges that might arise. Choosing a contractor with proven experience in insulated siding installation ensures a high-quality result that meets industry standards and maximizes the long-term benefits of the investment. A poorly executed installation can compromise the energy efficiency, durability, and aesthetic appeal of the siding.
Environmental Impact
Insulated siding, while offering numerous benefits, carries an environmental footprint stemming from its manufacturing, use, and eventual disposal. Understanding this impact is crucial for making informed decisions about home improvement and contributing to environmental sustainability. This section examines the environmental implications of various insulated siding materials and compares them to alternatives.
The environmental impact of insulated siding is multifaceted, encompassing the extraction of raw materials, manufacturing processes, transportation, installation, and ultimately, disposal or recycling. Different materials have varying degrees of impact, influencing the overall environmental footprint of the product throughout its lifecycle.
Manufacturing and Disposal of Insulated Siding Materials
The manufacturing process for insulated siding materials consumes energy and resources, and generates waste. For example, vinyl siding, a popular choice, is derived from petroleum, a non-renewable resource. Its production involves energy-intensive processes, leading to greenhouse gas emissions. Disposal of vinyl siding can also be problematic, as it is not easily biodegradable and often ends up in landfills. Fiber cement siding, while more durable, requires significant energy for manufacturing and involves the use of cement, which has its own carbon footprint. On the other hand, some insulated siding options utilize recycled materials, potentially reducing the environmental impact compared to those made entirely from virgin resources. The disposal of these materials varies depending on their composition; some may be recyclable, while others may require specialized disposal methods.
Comparison of Insulated Siding to Other Siding Options
Comparing the environmental footprint of insulated siding to other options, such as wood, metal, or brick, requires considering the entire lifecycle. Wood siding, for instance, is a renewable resource, but its harvesting and processing can still have environmental consequences, including deforestation and transportation emissions. Metal siding, often made from steel or aluminum, requires significant energy for production and has a substantial carbon footprint associated with its mining and processing. Brick siding, while durable, necessitates the extraction and firing of clay, resulting in energy consumption and air pollution. The overall environmental impact of each siding option depends on various factors, including material sourcing, manufacturing processes, transportation distances, and end-of-life management. A comprehensive life cycle assessment (LCA) can help compare the environmental performance of different siding options.
Sustainable and Recyclable Insulated Siding Materials
Choosing sustainable and recyclable insulated siding materials is a key step in minimizing environmental impact. Products made with recycled content, such as recycled plastic or wood fibers, reduce reliance on virgin resources and lessen the demand for new material extraction. Furthermore, selecting siding that is itself recyclable at the end of its life extends the material’s useful lifespan and reduces landfill waste. For example, some manufacturers are developing siding materials incorporating recycled plastics, offering a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional vinyl siding. The availability and cost of these sustainable options may vary, but their contribution to environmental responsibility is significant. Consumers should seek out products with certifications or labels indicating their sustainability and recyclability.
Conclusion
Ultimately, the question of whether insulated siding is “worth it” depends on individual circumstances and priorities. While the initial investment may be higher than traditional siding, the potential long-term savings in energy costs, coupled with increased home value and improved aesthetics, can make it a worthwhile investment for many homeowners. A thorough cost-benefit analysis, considering your specific climate, home size, and personal preferences, is crucial in making an informed decision. By carefully weighing the factors discussed, you can confidently determine if insulated siding is the right choice for your home.